Halt & Hass Test Chambers Manufacturer
HALT and HASS Test Chambers from WEIBER provide extreme temperature & vibration capabilities used during the product design and manufacturing cycles to compress the time normally required to identify design and process weaknesses. HALT techniques are important in uncovering many of the weak links inherent to the design and fabrication process of a new product. HASS techniques are incorporated during the production phase to find manufacturing process defects that could cause product failures in the field.

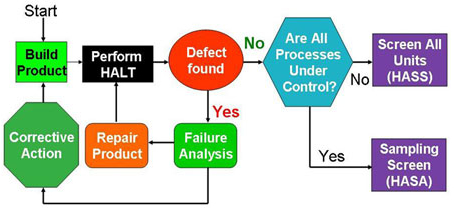
What is a Hass Chamber?
A HASS (Highly Accelerated Stress Screening) chamber is a specialized environmental testing system designed to rapidly expose products to extreme thermal and vibration stresses. Its purpose is to uncover latent manufacturing defects that might not appear under normal testing conditions.
What is the Difference Between Hass and Halt Testing?
Highly Accelerated Life Testing (HALT) and Highly Accelerated Stress Screening (HASS) are advanced reliability testing methods with distinct roles in product development and manufacturing. HALT testing is performed during the design phase to identify and eliminate design flaws by pushing products beyond their operational limits through extreme temperature variations and intense vibration, ensuring maximum durability and performance. HASS testing, applied during production, uses controlled stress levels determined from HALT to detect latent manufacturing defects without harming functional units, guaranteeing consistent product quality and reliability in mass production. Together, HALT and HASS improve product robustness, reduce failures, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Halt/Hass Testing Standards
HALT (Highly Accelerated Life Testing) and HASS (Highly Accelerated Stress Screening) follow qualitative standards aimed at enhancing product reliability rather than predicting exact lifespan. The most widely recognized guideline is IEST-RP-PR003, issued by the Institute of Environmental Sciences and Technology (IEST), which defines best practices, equipment specifications, stress profiles, and fixturing requirements for both testing methods. HALT testing pushes products to failure during the design phase to uncover weaknesses, while HASS testing applies HALT-derived limits in production to detect manufacturing defects without damaging good units. By following these standards, manufacturers can improve product robustness, reduce warranty costs, and maintain consistent quality in mass production.